Decreased level of consciousness or an alteration in sensorium or orientation may be an indicator of a hypoperfusion or low cardiac output state.
• Sensorium, orientation
• Weakness, fatigue
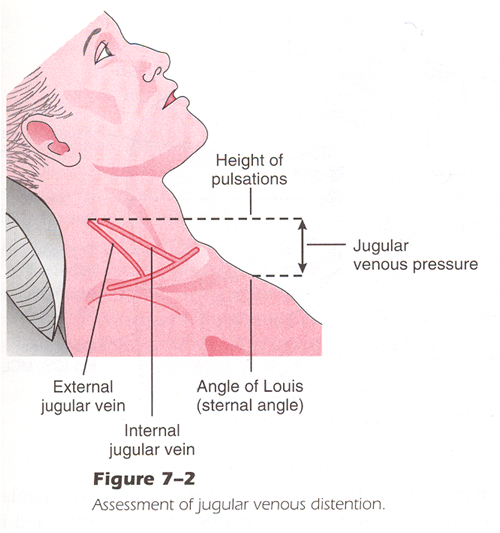
• JVD
JVD is an indicator of fluid status (overloaded or hypovolemic) and would correlate with an elevated CVP.
• Jugular veins normally are fully distended when lying flat in bed
• Normal: absence of JVD with HOB at 30 degrees or higher
• Abnormal to severe: JVD increased with HOB elevated 30 degrees or higher
These are the landmarks for assessing JVD: the identification of internal and external jugular veins, the angle of Louis, and the elevation of the venous distention.
Bucher, L. & Melander, S. (1999). Critical Care Nursing
When a patient is in pain, the stress response is activated. This increases the heart rate, the blood pressure, SVR and as a result, the workload is increased As a result increased myocardial oxygen consumption occurs. This causes an imbalance between oxygen supply and demand which may cause hypoxemia and possibly ischemia. Give analgesics as indicated.
Poorly controlled pain may result in a sympathetic response that can affect the cardiovascular system. This may result in increased heart rate, cardiac output, blood pressure, SVR, increased cardiac workload and myocardial oxygen consumption. The diastolic filling time decreases with an elevated heart rate resulting in an imbalance between myocardial oxygen demand and supply causing hypoxemia or ischemia (Watt-Watson & Stevens, 1998).
• Assessment
• Hemodynamic effects
• Effects of pain interventions