This is a brief overview of cardiac anatomy, physiology, and function.
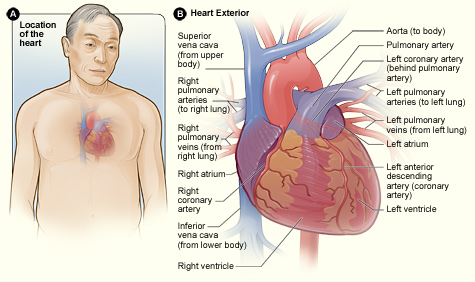
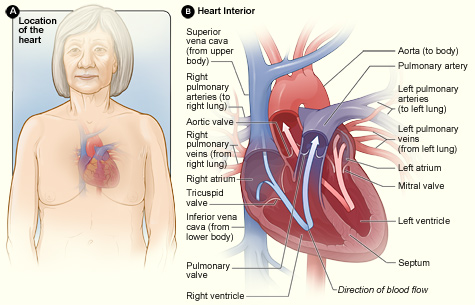
• Continuous, closed, fluid-filled, elastic circuit equipped with a pump
• Heart: pump which forces blood through the vascular system
• Arteries: conduits that deliver cardiac output (oxygenated blood) through the body, and to the organs, regulated by metabolic need
• Capillaries: micro-vessels where exchange of gases, nutrients, & metabolites occurs between plasma & body cells
• Veins: conduits that return deoxygenated blood to the heart
•reservoir: accommodates 70% of circulating blood volume
•Blood: liquid medium in which the respiratory gases, nutrients, metabolic wastes, & hormones are dissolved, and the formed elements of blood (RBCs, WBCs, & platelets) are carried