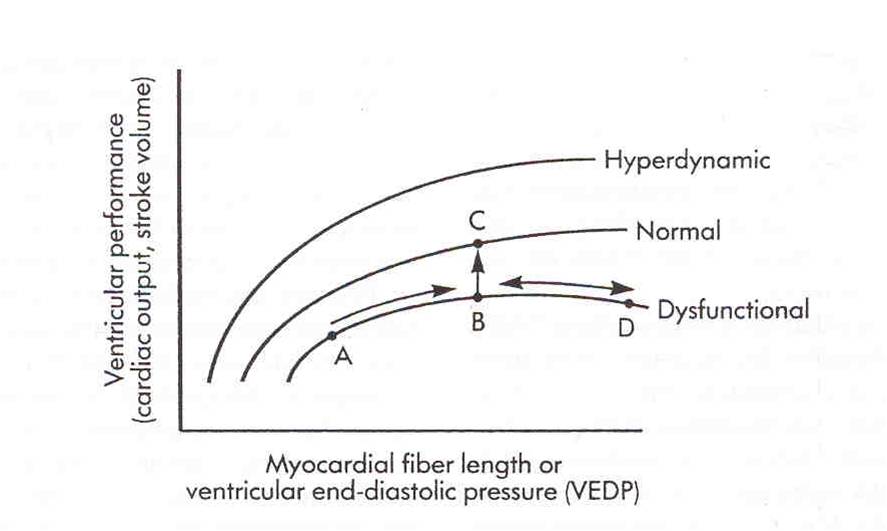
• Increase in the end-diastolic myocardial fiber length increases the tension of the myocardial fiber
• If ventricular end-diastolic pressure is increased using fluids, stroke volume and cardiac are increased
• Dysfunctional myocardium will require more volume to increase cardiac output that normal myocardium
• Excessive volume can produce decreased cardiac output and then diuretic or vasodilator may be indicated
• Hyperdynamic myocardium will produce a high cardiac output even in a low volume state
• Ventricular compliance affects cardiac output in response to fluids
• Non-compliant or "stiff" ventricle will respond to small increases in fluids
• Extremely compliant ventricles can tolerate large volumes of fluids, and fluid challenges may produce minimal change in output