• Symptoms
• Chest pain: angina, pericarditis
• Heart Sounds
• rate
• rhythm
• quality
Cardiac tamponade is caused by fluid or blood collecting in the pericardium resulting in compression of the heart. This inhibits the heart from filling adequately and ejecting a normal cardiac output. Assessment of heart tones hourly allows the nurse to determine if tamponade may be occurring. Heart tones will diminish with tamponade. Pulse pressure decreases because of the compression of the heart. Systolic pressure is lower because of the lower cardiac output, diastolic pressure is higher because of the compression. Increased CVP is a result of the inability of the right atrium to empty into the ventricle. Tachycardia is compensatory for low cardiac output.
• May be acute or gradual
• Diminished heart sounds
• Narrowed pulse pressure (SBP-DBP)
• Increased CVP
• Tachycardia
• Signs & symptoms of decreased cardiac output
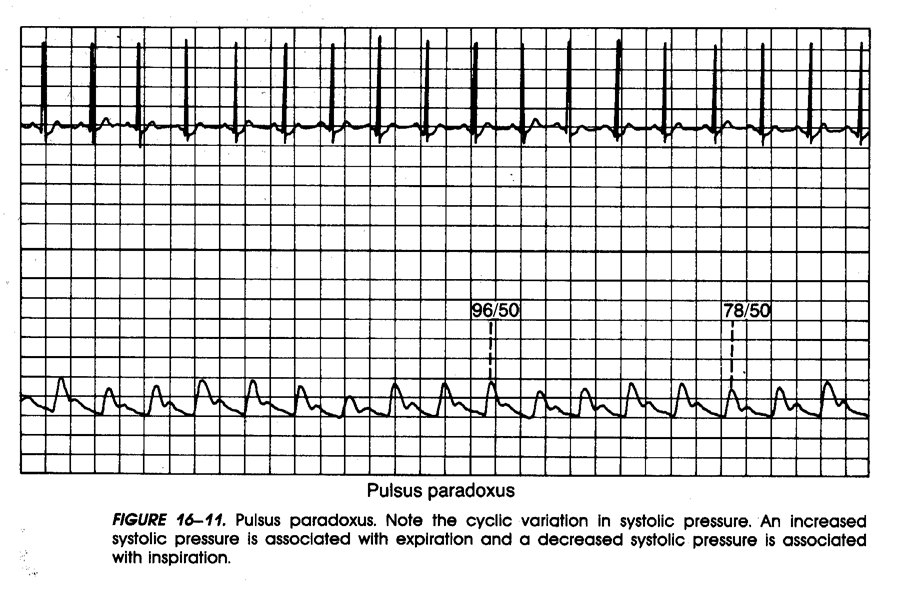
• Pulsus paradoxus: Caused by a decrease in pulse volume during inspiration and increase during expiration
Pulsus paradoxus is caused by the increased pressure in the thoracic cavity during inspiration, when cardiac tamponade is present. This can be seen on the arterial pressure waveform. Note the respiratory artifact and variation in blood pressure. Also, note the low pressures related to the decreased cardiac output.
• Intermittent sounds correlate with expiration
• Slowly deflate cuff until all sounds auscultated thru breathing cycle
• Pressure difference between phasic and consistent sounds is the measure
• Variability of 5-10mm Hg is significant
• May also be visible on SaO2 waveform
This is an emergency situation and the physician must be notified immediately! Elevating the head of the bed helps to empty the atria empty into the ventricles to improve cardiac output. Fluids will increase preload to help improve cardiac output. If the condition is bleeding from a surgical procedure, the patient may need to go back to surgery. If the condition occurs over a period of time, a pericardiocentesis or pericardial window may be performed.
• Elevate HOB to 20 degrees
• Rapidly infuse fluids
• increase preload
• notify physician
• pericardiocentesis
• back to OR if cardiac surgery
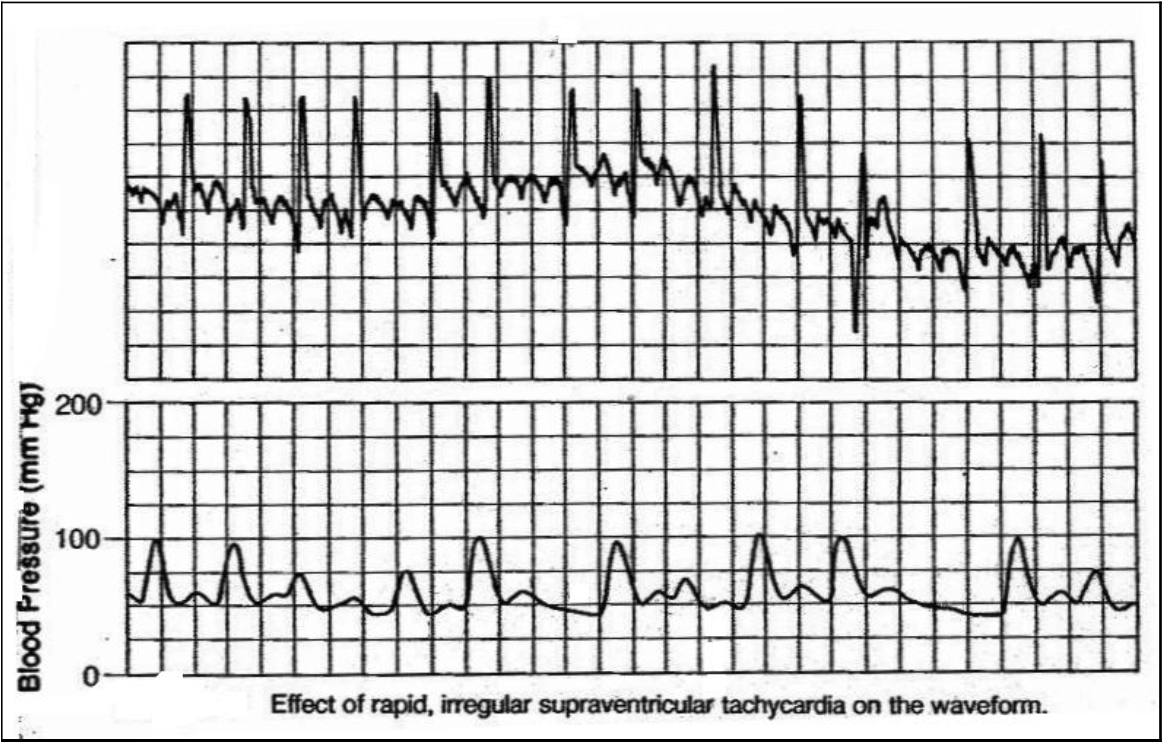
Consider the effects of the rhythm on the cardiac output. If the patient is tachycardic, determine causation and treat as indicated based on signs and symptoms and assessment.
• Effects on cardiac output
• rhythm
• rate
• ectopy
Note in this arterial waveform the patient has atrial fibrillation with a rapid ventricular response. The filling time is variable because of the rhythm and rate, therefore decreased cardiac output can be visualized from the arterial pressure waveform.
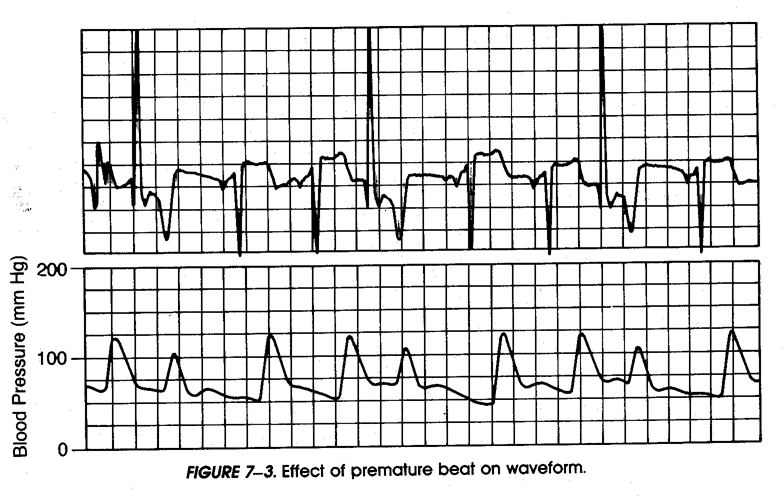
The same holds true when early ectopic beats occur resulting in decreased cardiac output. This beat may not perfuse.